
Electric Car Chargers: Types, Benefits, Prices
Electric car charger at your home or business. Take advantage and charge with your own charging station.
Types of chargers
What types of electric car chargers are there?

Types of chargers for electric cars.
Mainly, there are two types of chargers for electric cars: alternating current and direct current chargers, whose difference between these lies in whether the conversion of the alternating current energy from the network to direct current energy necessary to charge the electric car occurs within or out of it.
When charged with an AC charger, the conversion takes place inside the car. With limited space inside the converter, the size of the converter is also limited, so the maximum load capacity is between 1.4 kW and 43 kW. DC chargers perform the conversion outside the car, at the charging station. When outside of the vehicle, DC chargers can charge faster, up to 350 kW. Furthermore, electric car chargers can be divided into three levels, where level 1 is the slowest way of charging and level 3 is the fastest. Let's see them below:
⚡Level 1 charging is the slowest speed (max 3 kW: 5-20 hours) that would normally use a standard 10 amp power point. It is the most basic charge and allows to increase the useful life of the batteries. Its disadvantage is that the loading time is long.
⚡⚡Level 2 charging requires the installation of a specialized electric car charger at home (semi-fast charging 3 kW-22 kW: 1 to 4.5 hours). They can be found in parking lots of shopping centers, companies or on public roads. An example of these are the Wallbox chargers.
⚡⚡⚡Level 3 charging is fast charging (up to 150 kW: 5 to 30 minutes). It is the fastest type of charge, but also the most expensive, normally used by people who travel long distances, since they can add up to 720 km of range per hour. The best-known example of a Level 3 electric car fast charger is the Tesla SuperCharger.
Currently, there is another alternative (still under development) such as a portable charger system to recharge the electric car. It is a battery kit with its own plug that connects to the vehicle's current. It is useful to assist those who have been left without autonomy and do not have easy access to a charging station.
Charger compatibility
Charging stations have different sockets depending on the make of the car and the country where it is being charged. Still, most countries follow the following standards:
- AC charging standards
The Type 1 connector is the first connector that was made specifically for charging electric cars or vehicles. For American and most Asian cars, Type 1 intakes are standard. These single-phase plugs can deliver up to 7.4 kW of power and can support two levels of alternating current charging.
The Type 2 connector is the most widely used in Europe. It works with single-phase and three-phase installations. For European vehicles, Type 2 sockets are standard. These three-phase plugs can deliver up to 22 kW for private charging and up to 43 kW for public charging.
Likewise, the identifiers of the labels of the Spanish Association of Automobile and Truck Manufacturers (Anfac) for alternating current are B, C, D and E.

Table prepared by Anfac explaining the meaning.
- DC charging standards
The CHAdeMO charger (CHArge by MOve) is the most versatile and adaptable electric car charger. It is a three-phase charger that uses direct current with high speed and is bidirectional, which means that if necessary, the car can become a supplier of electrical energy. Asia leads the way in the manufacture of electric cars compatible with CHAdeMO plugs, widely used in Japan. Allows high power charging up to 100 kW.
GB/T charger is the Chinese standard for charging electric cars. It offers up to 237.5 kW.
For direct current, the identifiers/labels are K, L, M, N, and O.

Table prepared by Anfac explaining the meaning.
- There are also other types of connectors:
The unique combined charger, which charges both with alternating and direct current. The CCS is standard for European (CCS2) and North American (CCS1) car manufacturers. It can grant up to 350 kW of power.
In addition, there are technologies that will be further developed in the future, such as wireless charging that is carried out by means of induction or magnetic resonance.
On the other hand, Tesla, for example, has launched the J1772 plug, which is a charger compatible with all electric cars so that any electric vehicle regardless of brand, can use them to recharge. Regarding the portable charger for Nissan Leaf, the world's best-selling electric vehicle, after the first model with 24 kWh and its upgrade to 30 kWh, the Nissan Leaf is available with a 40 kWh battery and the Leaf e+ 62 kWh model. The Leaf uses two charging inputs: Type 2 connector and CHAdeMO, seen above.
Charger brands

Different electric car chargers.
When you consider buying an electric car, you not only assess what make and model it will be, but also what infrastructure it will need, for example, to carry out the charge. Although the public charging network is expanding, home charging is the most convenient and viable option. It is important to know the characteristics of the electrical installation of the house, single-phase or three-phase, since this also conditions the type of car charger.
There are several options on the market to choose your electric car charger. These are the most popular currently (in alphabetical order):
- ABB charger, Terra AC model, with 7.4 kW power.
- Cargatucoche, Stellar model, 7.4 kW of power.
- Circutor, eHome model, 7.4 kW power.
- EvBox, EvBox Elvi model, 7.4 kW power.
- Orbis, Orbis Viaris Uni model, 7.4 kW power.
- Policharger, Policharger Pro model, 7.4 kW power.
- Schneider, EVLink Smart model, 7.4 kW power.
- Simon, Simon model, 7.4 kW power.
- Veltium, Lite Zero model, 7.4 kW power.
- Wallbox, Pulsar Plus model, 7.4 kW power.
In addition, we can mention the Tesla Supercharger, with its different types of charging:
- Slow: 19 hours - 3.5 kWh
- Semi-rapid: 4 hours - 11 kWh
- Fast: 1.30 hours - 50 kWh
- Super fast: 30 minutes - 150 kW
Installation of chargers
How to install an electric car charger at home?

Installation of charger for electric car at home.
In the case of residing in an apartment and carrying out the installation in the community garage, you will find the bases of the process in the "Complementary Technical Instruction" ITC BT 52 for installations with special purposes - infrastructure for recharging electric vehicles.
If you want to install the charging point in your parking space (and the garage and the apartment you live in are in the same block), you must first inform the community. It is enough to inform in a protocol manner, since according to the Horizontal Property Law said installation is not submitted to the approval of the neighborhood council. In this case, the regulations allow laying a cable from the household meter to the parking space. With this system it is not necessary to register a new supply point.
If the parking space is not in the same building where the apartment is located, unlike the previous case, you will have to first request permission from the community of owners and that they approve the possibility of connecting a charging point in a neighborhood meeting.
On the other hand, in the case of residing in a single-family home, there is more freedom to install the charging point both outdoors and indoors, as well as on the wall (wallbox in English) or not. It's up to you!
The best thing and what the regulations indicate is to install an exclusive circuit from the house meter to the one where the charging point is located, to improve the safety of said installation. This must be well dimensioned, with electrical protections and charging points that can withstand the current.
To calculate the power (kW) that is going to be needed, the number of electrical appliances that can be used at the same time together with the installation of the charging point must be taken into account, without tripping the differential.
Charger costs
What is the price of an electric car charger?
As is usually the case, the prices of chargers vary and are conditioned by some factors such as the quality of the materials, the power, the length of the cable, or if, for example, it has outdoor protection. In any case, it can be said that the average is between €500 and €1,000.
From the examples of brand chargers for electric cars seen above, we find the following prices -these do not include installation nor the help that the Moves III Plan offers for the installation of charging points that we will see later-:
- ABB charger, Terra AC model, €1,140
- Cargatucoche, Stellar model, €775
- Circutor, eHome model, €525
- EvBox, EvBox Elvi model, €700
- Orbis, Orbis Viaris Uni model, €850
- Policharger, Policharger Pro model, €859
- Schneider, EVLink Smart model, €1,500
- Simon, Simon model, €925
- Veltium, Lite Zero model, €590
- Wallbox, Pulsar Plus model, €599
The current Moves III Plan is a plan that adds to the help to purchase an electric car, and also consists of an incentive for the installation of charging points. Subsidize up to 70% of the cost of the points of recharge (for individuals and for community of neighbors). The discount reaches 80% in localities with less than 5,000 inhabitants. The deadline to opt for said Plan is December 31, 2023.
What is the cost of installing a charging point at home?
There is no single answer. The price of the installation depends on several factors, such as the cable (mainly the length and thickness), and whether or not it includes a reset system. In any case, it could be said that the average price of installing an electric car charger in neighborhood communities is above €1,200 plus VAT, and €850 plus VAT for single-family homes. It is recommended to rule out installation budgets that are less than €700.
Benefits of having a charger
Advantages and benefits of having an electric car charger at home

Advantages and benefits of having an electric car charger at home.
- Comfort and tranquility
By having your own charger at home, you will always have a charging point to go to. This is important due to the little infrastructure of chargers for electric cars that currently exists, although little by little there are more and more. In addition, charging the car at home is equivalent to not having to travel. You will do it when you need it and/or when your schedules allow it. If you have solar panels in your home, you can take advantage of your own energy generated from this renewable source, to charge the car and do it practically at zero cost during sunny hours. The savings will be greater!
- Security
With your own electric car charger, you can be sure that you are using the correct cable and that the equipment is in good condition. It will allow you to go out with a full battery, giving you maximum autonomy. An electric car charger is a safe option, which incorporates the protections that guarantee the correct functioning of the entire electrical installation, unlike the Schuko socket -whose socket is not sized to charge those amps for so many hours- which causes the wall socket from deteriorating and burning.
- Speed
To preserve the health of the car battery, it is best to carry out slow charges at home. Fast charging is better done in exceptional cases since its regular use deteriorates and degrades the battery prematurely. However, if you buy a charger with more power you can minimize charging times. For example, if you install a smart electric car charger in your home, recharging can be up to ten times faster than with a conventional one.
- Saving
Having a charger for your electric car at home will allow you to save as much as possible and not pay more money at public charging stations. In addition, many chargers can be programmed to use them when electricity rates are cheaper and even manage the charge through an application on your mobile. Although it depends on the electricity rate you have contracted, if you do not have a flat rate, for example, and you depend on the regulated market, the cheapest hours are usually those at night after 00:00.
Frequently asked questions about electric car chargers
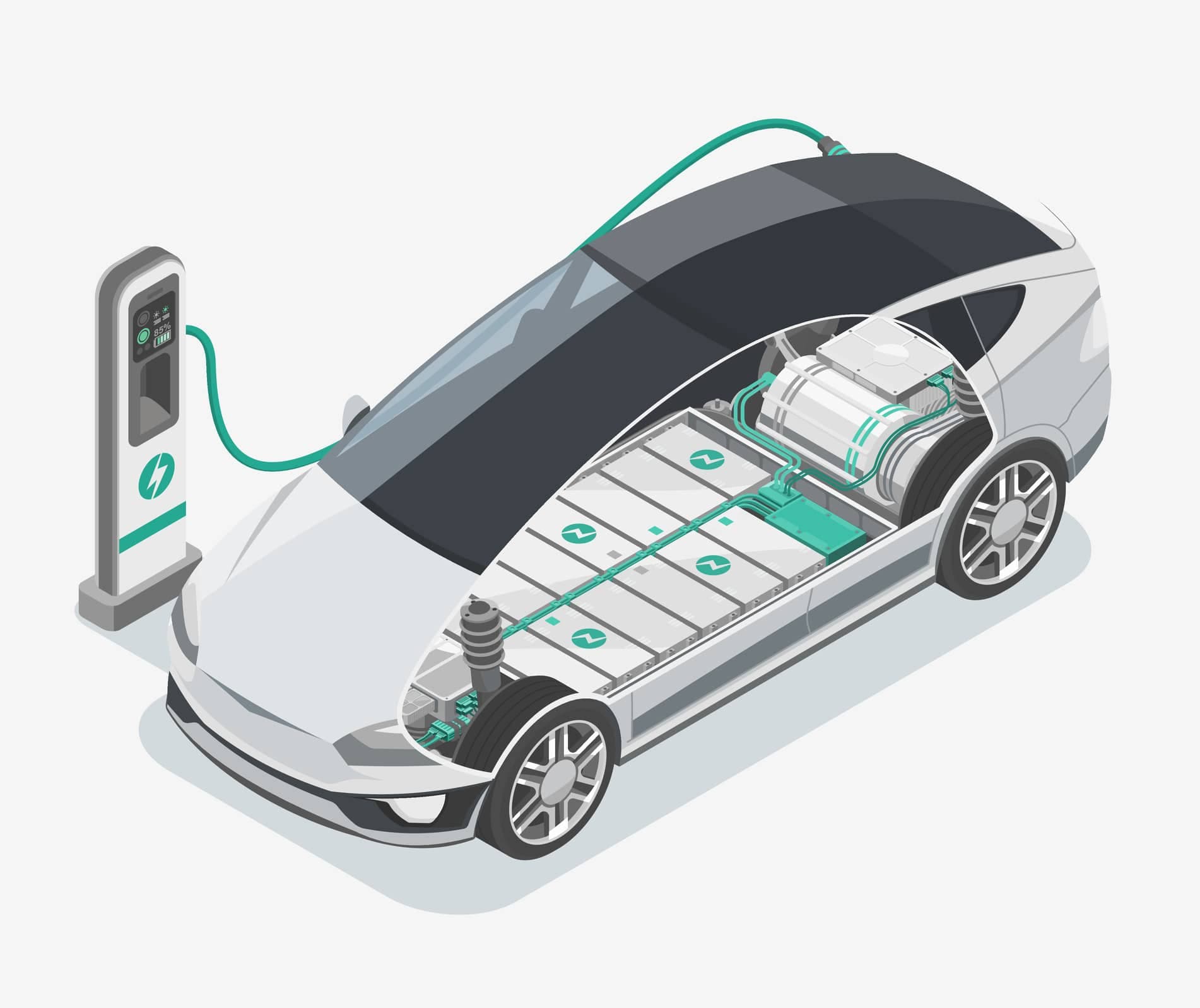
Operation of chargers for electric cars.
How does an electric car charger work?
By nature, power from the electrical grid is alternating current and electrical power from a battery is direct current. Therefore, to charge an electric vehicle from the grid, that power must be converted from alternating current to direct current. The converter integrated into an electric car charger will convert the energy into adequate energy to charge the vehicle's battery.
How long does it take to charge an electric car?
The time it takes to charge an electric car depends on the size of the battery and the speed of the vehicle's charger.
With direct current fast chargers from 50 kW to 350 kW, in 15 minutes and up to an hour, they can offer between 200 km and 500 km of autonomy.
Residential or commercial AC charging points between 7 kW and 22 kW take between 4 and 8 hours to charge.
What power do I need at home to charge an electric car?
How much power does an electric car need to charge?
The minimum charging power of electric cars is 2.3 kW. It is recommended to have at least 3.6 kW of power, but the most recommended and used option is to have a recharging point of 7.4 kW of power.
How many kW does an electric car charger need?
It is advisable to recharge an electric car using a charging power of 7.4 kW, which is what a wall charger offers you (wallbox). You will get a full charge in 5-6 hours.
What kind of plug does an electric car need?
The standard charger is the type 2 (Mennekes plug) usually found in European charging points. For loads greater than 43 kW of continuous current, a CCS or CHAdeMO type charger is necessary.

Installation of charger for electric car at home.
Although they are still in the development and growth stage, electric car chargers and self-consumption with solar panels are a perfect combination!
Request quotes here!
If you want more information about car chargers, request quotes with different installers without obligation here.
